Liang Yingzong

|
- 教授
- Supervisor of Doctorate Candidates
- Supervisor of Master's Candidates
- Name (English):Liang Yingzong
- Name (Pinyin):Liang Yingzong
- Date of Employment:2018-12-27
- School/Department:School of Materials and Energy
- Contact Information:yliang@gdut.edu.cn
- Professional Title:教授
- Status:On-the-job
- Alma Mater:The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
- Teacher College:School of Materials and Energy
- Discipline:工程热物理
 Contact Information
Contact Information
- ZipCode:
- PostalAddress:
- Telephone:
- Email:
- Paper Publications
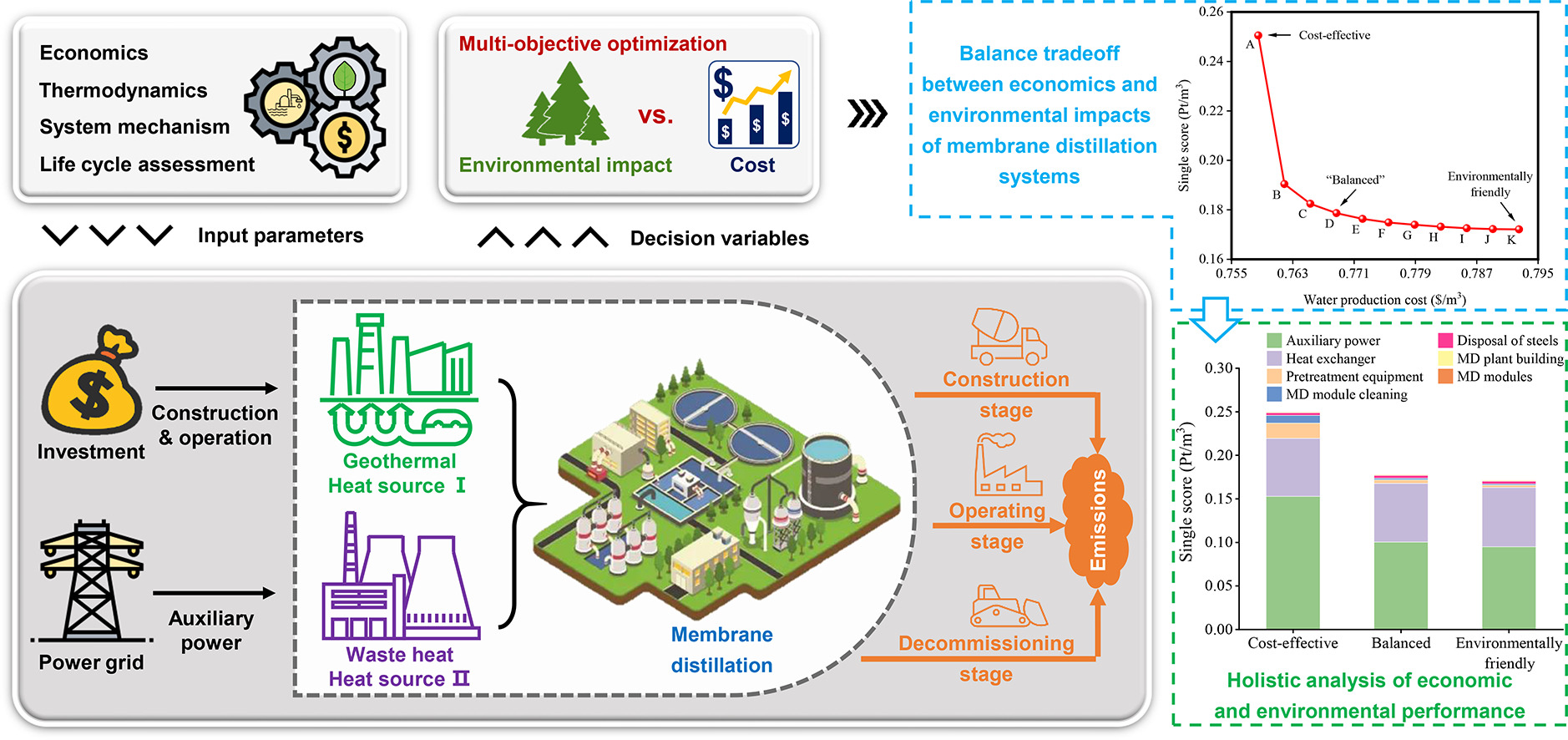
Techno-economic-environmental analysis of direct-contact membrane distillation systems integrated with low-grade heat sources: A multi-objective optimization approach
Release time:2023-07-23 Hits:
- Impact Factor:11.2
- Journal:Applied Energy
- Key Words:Membrane distillation (MD) is an emerging desalination technology powered by low-grade thermal energy. This paper presents the multi-objective optimal design of the membrane distillation desalination plant. The heat sources are supercritical CO2 (sCO2) Brayton cycle waste heat and geothermal energy. Multi-objective mixed-integer nonlinear programming models are developed to optimize the integrated systems' design and operating conditions based on economic and environmental metrics. The models consider the simultaneous optimization of water production costs (wpc) and environmental impacts (wpei). The environmental performance is quantified through a life cycle assessment using the widely used ReCiPe 2016 method, enabling the identification of the main environmental hotspots throughout the plant's life cycle. Our methodology demonstrates the sustainability of MD desalination plants through various case studies. The results indicate that an appropriate MD system design can significantly reduce the environmental burden with a slight increase in cost. For the sCO2-MD scenario, a cost-effective design can achieve a minimum wpc of 0.758 $/m3 and a minimum wpei of 0.172 Pt/m3 in an environmentally friendly design. A balanced design can reduce the environmental impact by 31.30% with a slight cost increase of 4.48% compared to a cost-effective design. The minimum wpc and minimum wpei for the geothermal MD (GTMD) scenario are 412.27% and 215.94% higher, respectively, compared to the sCO2-MD scenario. Moreover, reducing the wpei of the GTMD system is also more expensive, requiring a 10.67% increase in cost to reduce the environmental impact by 21.65%.
- Co-author:Jianyong Chen,Zhi Yang,Ying Chen
- First Author:Jianwei Xu
- Indexed by:Journal paper
- Correspondence Author:Yingzong Liang,Xianglong Luo
- Volume:349
- Page Number:121640
- Translation or Not:no
- Date of Publication:2023-11-01
- Included Journals:SCI