Liang Yingzong

|
- 教授
- Supervisor of Doctorate Candidates
- Supervisor of Master's Candidates
- Name (English):Liang Yingzong
- Name (Pinyin):Liang Yingzong
- Date of Employment:2018-12-27
- School/Department:School of Materials and Energy
- Contact Information:yliang@gdut.edu.cn
- Professional Title:教授
- Status:On-the-job
- Alma Mater:The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
- Teacher College:School of Materials and Energy
- Discipline:工程热物理
 Contact Information
Contact Information
- ZipCode:
- PostalAddress:
- Telephone:
- Email:
- Paper Publications
Decoding the performance of module-scale interfacial desalination from a thermodynamic perspective
Release time:2023-07-03 Hits:
- Impact Factor:9.9
- DOI number:10.1016/j.desal.2023.116818
- Journal:Desalination
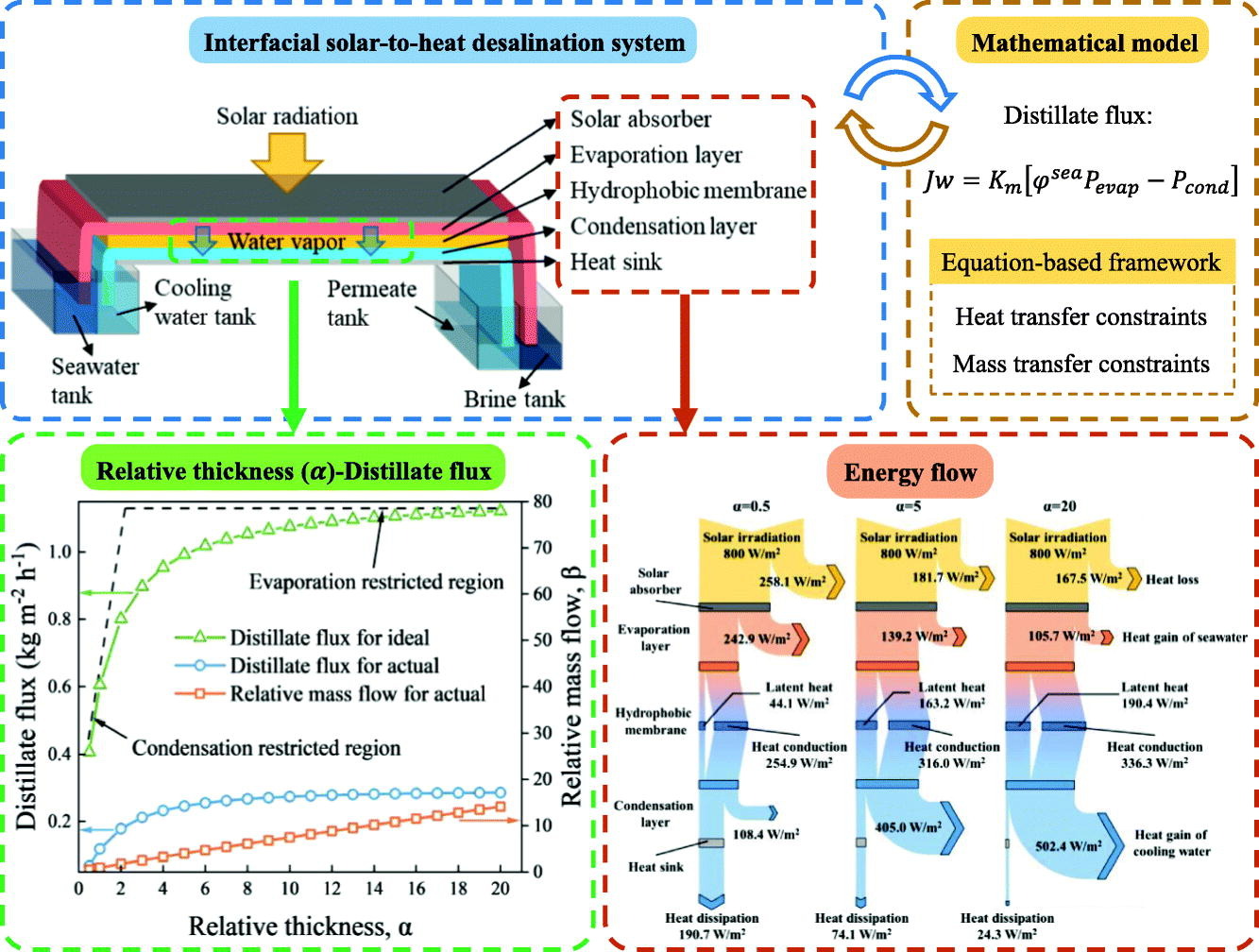
- Key Words:Passive solar-driven interfacial evaporation (PSDIE) is a highly efficient desalination technology that localizes heating at the evaporation surface, resulting in low heat loss and high evaporation rates. While many studies have focused on improving solar absorber performance, few have systematically analyzed the PSDIE thermodynamics. In this study, we propose a novel PSDIE distiller that effectively avoids salt accumulation. A module-scale model is developed that captures the mass and heat transfer characteristics of the distiller, and comprehensive thermodynamic analysis is performed. Our results show that the relative thickness between the evaporation and condensation layers, namely α, is a critical design parameter that optimizes process performance. An evaporation restricted region (α >5) and a condensation restricted region (α <5) can be identified. We also investigate the influence of hydrophobic membrane properties, finding that their effects depend on α. Our analysis demonstrates that inlet salinity of seawater feed has a detrimental effect on the water productivity of the distiller, while distiller with larger α tends to be more salt tolerable. Finally, we propose a design for a multistage distiller system and evaluate its water production performance, the results show that additional evaporation stages are beneficial to the distiller with smaller α.
- Co-author:Jiancong Ye,Xianglong Luo,Jianyong Chen,Zhi Yang,Jiacheng He
- First Author:Yingzong Liang
- Indexed by:Journal paper
- Correspondence Author:Ying Chen
- Volume:565
- Page Number:116818
- Translation or Not:no
- Date of Publication:2023-11-01
- Included Journals:SCI
Pre One:Techno-economic-environmental analysis of direct-contact membrane distillation systems integrated with low-grade heat sources: A multi-objective optimization approach
Next One:Integration and optimization of methanol-reforming proton exchange membrane fuel cell system for distributed generation with combined cooling, heating and power

